Friday, 28 October 2016
Tuesday, 27 September 2016
How to increase your website or Blog traffic
Hello Friends, I am going to share Jingling 4.0.2 Auto China Traffic Bot which can increase your website or Blog traffic. As you know that this software is very hard to find free and full version on internet because mostly user asking you to pay money. But here you can get free of charges for download you just need to complete one survey.
Tutorial
how to use this Jingling 4.0.2 Auto China Traffic Bot
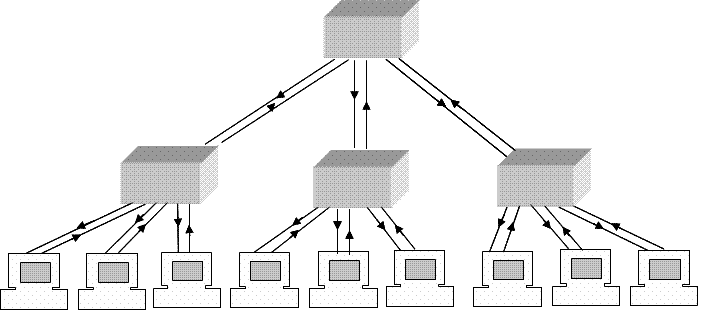
What is Hybrid Topology?
The hybrid topology is a type of network topology that is composed of one or more interconnections of two or more networks that are based upon different physical topologies
Note
- A Star ring network consists of two or more star topologies connected using a multistation access unit (MAU) as a centralized hub.
- A Star Bus network consists of two or more star topologies connected using a bus trunk (the bus trunk serves as the network's backbone).
What is Tree Topology?
Nodes in a tree are linked to a central hub that controls the traffic to the network. However not
every devices plugs directly into the central hub. The majority of devices connect to a secondary hub that in turn is connected to the central hub. The control hub in the tree is an active hub. An active hub
contains a repeater which is a hardware device that regenerates the received but patterns before sending them out. Repeating strengthens transmission & increases the distance a signal can travel.
Advantages Of Tree Topology:
• The distance to which a signal can travel increases as the signal passes through a chain of hubs.
• Tree topology allows isolating and prioritizing communications from different nodes.
• Tree topology allows for easy expansion of an existing network which enables organizations to configure anetwork to meet their needs.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology:
• If the backbone line breaks, the entire segment goes down.
• It is more difficult to configure and wire than other
topologies.
every devices plugs directly into the central hub. The majority of devices connect to a secondary hub that in turn is connected to the central hub. The control hub in the tree is an active hub. An active hub
contains a repeater which is a hardware device that regenerates the received but patterns before sending them out. Repeating strengthens transmission & increases the distance a signal can travel.
Advantages Of Tree Topology:
• The distance to which a signal can travel increases as the signal passes through a chain of hubs.
• Tree topology allows isolating and prioritizing communications from different nodes.
• Tree topology allows for easy expansion of an existing network which enables organizations to configure anetwork to meet their needs.
Disadvantages of Tree Topology:
• If the backbone line breaks, the entire segment goes down.
• It is more difficult to configure and wire than other
topologies.
What is Mesh Topology?
- Topology in which each of the nodes of the network is connected to each of the other nodes in the network with a point-to-point link – this makes it possible for data to be simultaneously transmitted from any single node to all of the other nodes.
- The physical fully connected mesh topology is generally too costly and complex for practical networks, although the topology is used when there are only a small number of nodes to be interconnected
• Advantages:
• Fault tolerance
• Guaranteed communication channel capacity
• Easy to troubleshoot
• Disadvantages:
• Difficulty of installation and reconfiguration
• Cost of maintaining redundant link
• The cost of cabling all the hosts together is expensive
What is Ring Topology?
- Topology in which each of the nodes of the network is connected to two other nodes in the network and with the first and last nodes being connected to each other, forming a ring
- All data that is transmitted between nodes in the network travels from one node to the next node in a circular manner and the data generally flows in a single direction only.
Advantages:
• Easy to install and wire.
• Because every computer is given equal access to the token, no one computer can monopolize the network.
Disadvantages:
• Requires more cable than a bus topology.
• If one computer fails it can affect the whole network.
• It is difficult to identify the problem if the entire network shuts down.
What is Star Topology?
- Topology in which each of the nodes of the network is connected to a central node with a point-to-point link in a "hub” or “Switch”
- All data that is transmitted between nodes in the network is transmitted to this central node
• Advantages:
- It is easy to modify and add new computers to a star network without disturbing the rest of the network.
- If one node or workstation (beside the middle node) goes down, the rest of the network will still be functional.
- The center of a star network is a good place to figure out where the network faults are located.
- You can use several cable types in the same network if the hub you have can handle multiple cable types.
• Disadvantages:
• Requires more cable than a bus topology.
• If the middle node goes down , then the entire network goes down.
• It is more expensive than because all cables must be connected to one central point.
What is Bus Topology?
In this type of network topology, all the nodes of a network are connected to a common transmission medium having two endpoints. All the data that travels over the network is transmitted through a common transmission medium known as the bus or the backbone of the network.
When the transmission medium has exactly two endpoints, the network topology is known by the name, 'linear bus topology'. In case the transmission medium, also called the network backbone, has more than two endpoints, the network is said to have a distributed bus topology.
Bus topology is easy to handle and implement and is best suited for small networks. But the downside of this topology is that the limited cable length limits the number of stations, thus limiting the performance to a less number of nodes.
When the transmission medium has exactly two endpoints, the network topology is known by the name, 'linear bus topology'. In case the transmission medium, also called the network backbone, has more than two endpoints, the network is said to have a distributed bus topology.
Bus topology is easy to handle and implement and is best suited for small networks. But the downside of this topology is that the limited cable length limits the number of stations, thus limiting the performance to a less number of nodes.
•advantage of network topology
1.The bus is simple, reliable in small network, easy to use and understand
2.Requires the least amount of cable to connect the computers and less expensive
3. Easy to extend the bus
•Disadvantage of network topology
1.Heavy network traffic can slow a bus considerably
2.Each barrel connector weakens the electrical signal
3. Difficult to troubleshoot a bus
What is Network Topology?
• A network topology describes the configuration of a network and the physical and logical arrangement of the nodes that form the network. There are two ways of defining network geometry: the physical topology and the logical (or signal) topology.
- Physical topology is the physical layout of the network, how the cables are arranged and how the computers are connected.
- Logical topology refers to the nature of the paths the signals follow from node to node.
Friday, 23 September 2016
Windows Server 2012 – An Overview
Greater flexibility and agility with Windows Server 2012 R2
At the heart of the Microsoft Cloud OS vision, Windows Server 2012 R2 brings Microsoft’s experience delivering global-scale cloud services into your infrastructure with new features and enhancements in virtualization, management, storage, networking, virtual desktop infrastructure, access and information protection, the web and application platform, and more.
windows Server 2012, codenamed "Windows Server 8" is the sixth release of Windows Server. It is the server version of Windows 8 and succeeds Windows Server 2008 R2. Two pre-release versions, a developer preview and a beta version, were released during development. The software was generally available to customers starting on September 4, 2012
Benefits
With Windows Server 2012 R2 you can scale to run your most important workloads with robust recovery options. You’ll achieve value quickly with a wide range of cost-effective, high-performance storage options and simplified delivery of multi-tenant IT services. You can build, deploy, operate, and monitor applications on premises and in the cloud. Empower users with secure access to corporate resources on the devices they choose.
Capabilities
Server virtualization
Take advantage of the cost savings of virtualization, and maximize server hardware investments by consolidating your servers as virtual machines on a single physical host. Hyper-V runs multiple operating systems including Windows, Linux, and others, in parallel, on a single server. Windows Server 2012 R2 extends Hyper-V’s capabilities with additional features and industry-leading scalability for host processors and memory.
Storage
Whatever your storage platform, the data it holds is the bedrock of your business. Windows Server 2012 R2 helps you optimize your existing storage investments, such as SANs. It also lets you build scalable, high-performance, highly available storage solutions using industry-standard hardware and Windows Server 2012 R2. Windows Server 2012 R2 helps ensure your storage remains continuously available, so your services can be, continuously available too.
Networking
You can manage an entire network as a single server, so you get the reliability and scalability of multiple servers at a lower cost. Automatic rerouting around storage, server, and network failures keeps file services online with minimal noticeable downtime. Together with System Center 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012 R2 can provide an end-to-end software defined networking solution across public, private, and hybrid cloud implementations.
Server management and automation
Following a standards-based management approach, the Windows Management Framework provides a common platform for automation and integration to help you automate your routine tasks with tools like Windows PowerShell. Other improvements help simplify deployment, ensure that the components of your datacenters have the correct configuration, and enable you to take action to manage across multiple servers through a single relevant dashboard in Server Manager.
Web and application platform
Windows Server 2012 R2 builds on the tradition of the Windows Server family as a proven application platform, with thousands of applications already built and deployed and a community of millions of knowledgeable and skilled developers already in place. You can build and deploy applications either on premises or in the cloud—or both at once, with hybrid solutions that work in both environments.
Access and information protection
With Microsoft's Access and Information Protection solutions, you can manage a single identity for each user, across both on-premises and cloud-based (SaaS) applications. You define a user’s level of access to information and applications each user has to information and applications based on who they are, what they are accessing, and from which device—, even applying multi-factor authentication. You can provide secure remote access to your mobile workers using the Windows Server Remote Access (RRAS) capabilities of DirectAccess and VPN (including automatic VPN connections) and enable your users to sync their work files from a corporate server to their devices. Also, you can manage mobile devices to remove corporate data and applications when a device is lost, stolen, or retired from use.
Virtual desktop infrastructure
With Windows Server 2012 R2, it's even easier to deploy and deliver virtual resources across devices. VDI technologies offer easy access to a rich, full-fidelity Windows environment running in the datacenter, from virtually any device. Through Hyper-V and Remote Desktop Services, Microsoft offers three flexible VDI deployment options in a single solution: Pooled Desktops, Personal Desktops, and Remote Desktop Sessions.
Services of server 2012
IP address management (IPAM)
Windows Server 2012 has an IP address management role for discovering, monitoring, auditing, and managing the IP address space used on a corporate network. The IPAM is used for the management and monitoring of Domain Name System (DNS) and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) servers. Both IPv4 and IPv6 are fully supported.
Active Directory
Windows Server 2012 has a number of changes to Active Directory from the version shipped with Windows Server 2008 R2. The Active Directory Domain Services installation wizard has been replaced by a new section in Server Manager, and a GUI has been added to the Active Directory Recycle Bin. Multiple password policies can be set in the same domain. Active Directory in Windows Server 2012 is now aware of any changes resulting from virtualization, and virtualized domain controllers can be safely cloned. Upgrades of the domain functional level to Windows Server 2012 are simplified; it can be performed entirely in Server Manager. Active Directory Federation Services is no longer required to be downloaded when installed as a role, and claims which can be used by the Active Directory Federation Services have been introduced into the Kerberos token. Windows Powershell commands used by Active Directory Administrative Center can be viewed in a "Powershell History Viewer".
Hyper-V
Windows Server 2012, along with Windows 8, includes a new version of Hyper-V, as presented at the Microsoft BUILD event. Many new features have been added to Hyper-V, including network virtualization, multi-tenancy, storage resource pools, cross-premise connectivity, and cloud backup. Additionally, many of the former restrictions on resource consumption have been greatly lifted. Each virtual machine in this version of Hyper-V can access up to 64 virtual processors, up to 1 terabyte of memory, and up to 64 terabytes of virtual disk space per virtual hard disk (using a new .vhdx format). Up to 1024 virtual machines can be active per host, and up to 8000 can be active per failover cluster. SLAT is a required processor feature for Hyper-V on Windows 8, while for Windows Server 2012 it is only required for the supplementary RemoteFX role.
ReFS
Main article: ReFS
Resilient File System (ReFS), codenamed "Protogon", is a new file system in Windows Server 2012 initially intended for file servers that improves on NTFS in some respects. Major new features of ReFS include:
Improved reliability for on-disk structures
ReFS uses B+ trees for all on-disk structures including metadata and file data. Metadata and file data are organized into tables similar to a relational database. The file size, number of files in a folder, total volume size and number of folders in a volume are limited by 64-bit numbers; as a result ReFS supports a maximum file size of 16Exabytes, a maximum of 18.4 × 1018 folders and a maximum volume size of 1 Yottabyte (with 64 KB clusters) which allows large scalability with no practical limits on file and folder size (hardware restrictions still apply). Free space is counted by a hierarchical allocator which includes three separate tables for large, medium, and small chunks. File names and file paths are each limited to a 32 KB Unicode text string.
Built-in resilience
ReFS employs an allocation-on-write update strategy for metadata, which allocates new chunks for every update transaction and uses large IO batches. All ReFS metadata has built-in 64-bit checksums which are stored independently. The file data can have an optional checksum in a separate "integrity stream", in which case the file update strategy also implements allocation-on-write; this is controlled by a new "integrity" attribute applicable to both files and directories. If nevertheless file data or metadata becomes corrupt, the file can be deleted without taking down the whole volume offline for maintenance, then restored from the backup. As a result of built-in resiliency, administrators do not need to periodically run error-checking tools such as CHKDSK when using ReFS.
Compatibility with existing APIs and technologies
ReFS does not require new system APIs and most file system filters continue to work with ReFS volumes. ReFS supports many existing Windows and NTFS features such as BitLocker encryption, Access Control Lists, USN Journal, change notifications, symbolic links, junction points, mount points, reparse points, volume snapshots, file IDs, and oplock. ReFS seamlessly integrates with Storage Spaces, a storage virtualization layer that allows data mirroring and striping, as well as sharing storage pools between machines. ReFS resiliency features enhance the mirroring feature provided by Storage Spaces and can detect whether any mirrored copies of files become corrupt using background data scrubbing process, which periodically reads all mirror copies and verifies their checksums then replaces bad copies with good ones.
Some NTFS features are not supported in ReFS, including named streams, object IDs, short names, file compression, file level encryption (EFS), user data transactions, hard links, extended attributes, and disk quotas. Sparse files was not supported by Preview, but it is supported by RTM. ReFS does not itself offer data deduplication. Dynamic disks with mirrored or striped volumes are replaced with mirrored or striped storage pools provided by Storage Spaces. However, in Windows Server 2012, automated error-correction is only supported on mirrored spaces, and booting from ReFS is not supported either.
IIS 8.0
Windows Server 2012 includes version 8.0 of Internet Information Services (IIS). The new version contains new features such as SNI, CPU usage caps for particular websites, centralized management of SSL certificates, WebSocket support and improved support for NUMA, but few other substantial changes were made.
Windows Server 2012 has an IP address management role for discovering, monitoring, auditing, and managing the IP address space used on a corporate network. The IPAM is used for the management and monitoring of Domain Name System (DNS) and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) servers. Both IPv4 and IPv6 are fully supported.
Active Directory
Windows Server 2012 has a number of changes to Active Directory from the version shipped with Windows Server 2008 R2. The Active Directory Domain Services installation wizard has been replaced by a new section in Server Manager, and a GUI has been added to the Active Directory Recycle Bin. Multiple password policies can be set in the same domain. Active Directory in Windows Server 2012 is now aware of any changes resulting from virtualization, and virtualized domain controllers can be safely cloned. Upgrades of the domain functional level to Windows Server 2012 are simplified; it can be performed entirely in Server Manager. Active Directory Federation Services is no longer required to be downloaded when installed as a role, and claims which can be used by the Active Directory Federation Services have been introduced into the Kerberos token. Windows Powershell commands used by Active Directory Administrative Center can be viewed in a "Powershell History Viewer".
Hyper-V
Windows Server 2012, along with Windows 8, includes a new version of Hyper-V, as presented at the Microsoft BUILD event. Many new features have been added to Hyper-V, including network virtualization, multi-tenancy, storage resource pools, cross-premise connectivity, and cloud backup. Additionally, many of the former restrictions on resource consumption have been greatly lifted. Each virtual machine in this version of Hyper-V can access up to 64 virtual processors, up to 1 terabyte of memory, and up to 64 terabytes of virtual disk space per virtual hard disk (using a new .vhdx format). Up to 1024 virtual machines can be active per host, and up to 8000 can be active per failover cluster. SLAT is a required processor feature for Hyper-V on Windows 8, while for Windows Server 2012 it is only required for the supplementary RemoteFX role.
ReFS
Main article: ReFS
Resilient File System (ReFS), codenamed "Protogon", is a new file system in Windows Server 2012 initially intended for file servers that improves on NTFS in some respects. Major new features of ReFS include:
Improved reliability for on-disk structures
ReFS uses B+ trees for all on-disk structures including metadata and file data. Metadata and file data are organized into tables similar to a relational database. The file size, number of files in a folder, total volume size and number of folders in a volume are limited by 64-bit numbers; as a result ReFS supports a maximum file size of 16Exabytes, a maximum of 18.4 × 1018 folders and a maximum volume size of 1 Yottabyte (with 64 KB clusters) which allows large scalability with no practical limits on file and folder size (hardware restrictions still apply). Free space is counted by a hierarchical allocator which includes three separate tables for large, medium, and small chunks. File names and file paths are each limited to a 32 KB Unicode text string.
Built-in resilience
ReFS employs an allocation-on-write update strategy for metadata, which allocates new chunks for every update transaction and uses large IO batches. All ReFS metadata has built-in 64-bit checksums which are stored independently. The file data can have an optional checksum in a separate "integrity stream", in which case the file update strategy also implements allocation-on-write; this is controlled by a new "integrity" attribute applicable to both files and directories. If nevertheless file data or metadata becomes corrupt, the file can be deleted without taking down the whole volume offline for maintenance, then restored from the backup. As a result of built-in resiliency, administrators do not need to periodically run error-checking tools such as CHKDSK when using ReFS.
Compatibility with existing APIs and technologies
ReFS does not require new system APIs and most file system filters continue to work with ReFS volumes. ReFS supports many existing Windows and NTFS features such as BitLocker encryption, Access Control Lists, USN Journal, change notifications, symbolic links, junction points, mount points, reparse points, volume snapshots, file IDs, and oplock. ReFS seamlessly integrates with Storage Spaces, a storage virtualization layer that allows data mirroring and striping, as well as sharing storage pools between machines. ReFS resiliency features enhance the mirroring feature provided by Storage Spaces and can detect whether any mirrored copies of files become corrupt using background data scrubbing process, which periodically reads all mirror copies and verifies their checksums then replaces bad copies with good ones.
Some NTFS features are not supported in ReFS, including named streams, object IDs, short names, file compression, file level encryption (EFS), user data transactions, hard links, extended attributes, and disk quotas. Sparse files was not supported by Preview, but it is supported by RTM. ReFS does not itself offer data deduplication. Dynamic disks with mirrored or striped volumes are replaced with mirrored or striped storage pools provided by Storage Spaces. However, in Windows Server 2012, automated error-correction is only supported on mirrored spaces, and booting from ReFS is not supported either.
IIS 8.0
Windows Server 2012 includes version 8.0 of Internet Information Services (IIS). The new version contains new features such as SNI, CPU usage caps for particular websites, centralized management of SSL certificates, WebSocket support and improved support for NUMA, but few other substantial changes were made.
Types of Computer Networks
A personal area network (PAN):
A personal area network (PAN) is a computer network used for data transmission among devices such
as computers,telephones and personal digital assistants. PANs can be used for communication among the personal devices themselves (intrapersonal communication), or for connecting to a higher level
network and the Internet.
• Local Area Network (LAN):
A local area network is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, or office building, using network media.
A personal area network (PAN) is a computer network used for data transmission among devices such
as computers,telephones and personal digital assistants. PANs can be used for communication among the personal devices themselves (intrapersonal communication), or for connecting to a higher level
network and the Internet.
• Local Area Network (LAN):
A local area network is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a home, school, computer laboratory, or office building, using network media.
A local area network (LAN) is a group of computers and associated devices that share a common communications line or wireless link to a server. Typically, a LAN encompasses computers and peripherals connected to a server within a distinct geographic area such as an office or a commercial establishment. Computers and other mobile devices use a LAN connection to share resources such as a printer or network storage.
• Metropolitan Area Network or MAN:
A metropolitan area network is used to connect multiple LAN's in a larger geographical area, such as a city or stat. this type of networks is mostly used by large cooperation's to connect the headquarter with otherbranches.
A metropolitan area network (MAN) is a network that interconnects users with computer resources in a geographic area or region larger than that covered by even a large local area network (LAN) but smaller than the area covered by a wide area network (WAN).
• Wide Area Network (WAN):
The wide area network, is the largest form of networks that we have, it connect other smaller networks with each other. The larges WAN is theinternet as it connects other networks world wide.
A computer network that spans a relatively large geographical area. Typically, a WAN consists of two or more local-area networks (LANs). Computers connected to a wide-area network are often connected through public networks, such as the telephone system. They can also be connected through leased lines or satellites.
• WLAN - Wireless Local Area Network:
The WLAN is a LAN that uses a WIFI connection to communicate.
• SAN - Storage Area Network:
The storage, System or Server Area Network, are networks that connects servers to storage devices
using high speed connection such as optic fibers.
Thursday, 22 September 2016
Saturday, 17 September 2016
Features of windows server 2012
Installation options
Unlike its predecessor, Windows Server 2012 can switch between "Server Core" and "Server with a GUI" installation options without a full reinstallation. Server Core - an option with a command-line interface only - is now the recommended configuration. There is also a third installation option that allows some GUI elements such as MMC and Server Manager to run, but without the normal desktop, shell or default programs like File Explorer.
User interface
Server Manager has been redesigned with an emphasis on easing management of multiple servers. The operating system, like Windows 8, uses the Metro-based user interface unless installed in Server Core mode. Windows Store is available in this version of Windows but is not installed by default.[18] Windows PowerShell in this version has over 2300 commandlets, compared to around 200 in Windows Server 2008 R2.
Task Manager
Main article: Windows Task Manager
Windows Server 2012 includes a new version of Windows Task Manager together with the old version. In the new version the tabs are hidden by default showing applications only. In the new Processes tab, the processes are displayed in varying shades of yellow, with darker shades representing heavier resource use. It lists application names and status, as well as CPU, memory, hard disk and network utilization. The process information found in the older versions are now moved to the new Details tab. The Performance tab shows "CPU", "Memory", "Disk", "Wi-Fi" and "Ethernet" graphs. The CPU tab no longer displays individual graphs for every logical processor on the system by default; instead, it can display data for each NUMA node. When displaying data for each logical processor for machines with more than 64 logical processors, the CPU tab now displays simple utilization percentages on heat-mapping tiles. The color used for these heat maps is blue, with darker shades again indicating heavier utilization. Hovering the cursor over any logical processor's data now shows the NUMA node of that processor and its ID, if applicable. Additionally, a new Startup tab has been added that lists startup applications, however this tab does not exist in Windows Server 2012. The new task manager recognizes when a Windows Store app has the "Suspended" status.
Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET)
ARPANET
Promoted to the head of the information processing office at ARPA,
Robert Taylor intended to realize Licklider's ideas of an interconnected
networking system. Bringing in Larry Roberts from MIT, he initiated a
project to build such a network. The first ARPANET link was
established between the University of California, Los Angeles and the
Stanford Research Institute on 21 November 1969. By 5 December
1969, a 4-node network was connected by adding the
University of Utah and the University of California, Santa Barbara.
Building on ideas developed in ALOHAnet, the ARPANET started in
1972 and was growing rapidly by 1981. The number of hosts had
grown to 213, with a new host being added approximately every twenty
days.
Computer network
• History
• In the 1960s, the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA)
started funding the design of the Advanced Research Projects
Agency Network (ARPANET) for the United States Department
of Defense. Development of the network began in 1969, based on
designs developed during the 1960s. The ARPANET evolved into
the modern Internet.
• In the 1960s, the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA)
started funding the design of the Advanced Research Projects
Agency Network (ARPANET) for the United States Department
of Defense. Development of the network began in 1969, based on
designs developed during the 1960s. The ARPANET evolved into
the modern Internet.
Saturday, 10 September 2016
About Windows server 2012
Windows Server 2012, codenamed "Windows Server 8" is the sixth release of Windows Server. It is the server version of Windows 8 and succeeds Windows Server 2008 R2. Two pre-release versions, a developer preview and a beta version, were released during development. The software was generally available to customers starting on September 4, 2012.
Unlike its predecessor, Windows Server 2012 has no support for Itanium-based computers and has four editions. Various features were added or improved over Windows Server 2008 R2 (with many placing an emphasis on cloud computing), such as an updated version of Hyper-V, an IP address management role, a new version of Windows Task Manager, and ReFS, a new file system. Windows Server 2012 received generally good reviews in spite of having included the same controversial Metro-based user interface seen in Windows 8.
The successor to Windows Server 2012, called Windows Server 2012 R2, was released along with Windows 8.1 in October 2013. A service pack, formally designated Windows Server 2012 R2 Update, was released in April 2014
History
Windows Server 2012, codenamed "Windows Server 8" is the sixth release of Windows Server family of operating systems developed concurrently with Windows 8.It was not until April 17, 2012 that the company announced that the final product name would be "Windows Server 2012"
Microsoft introduced Windows Server 2012 and its developer preview in the BUILD 2011 conference on September 9, 2011. However, unlike Windows 8, the developer preview of Windows Server 2012 was only made available to MSDN subscribers. It included a graphical user interface (GUI) based on Metro design language and a new Server Manager, a graphical application used for server management. On February 16, 2012, Microsoft released an update for developer preview build that extended its expiry date from April 8, 2012 to January 15, 2013.
Before Windows Server 2012 was finalized, two test builds were made public. A public beta version of Windows Server 2012 was released along with the Windows 8 Consumer Preview on February 29, 2012. The release candidate of Windows Server 2012 was released on May 31, 2012, along with the Windows 8 Release Preview.
The product was released to manufacturing on August 1, 2012 and became generally available on September 4, 2012. However, not all editions of Windows Server 2012 were released at the same time. Windows Server 2012 Essentials was released to manufacturing on October 9, 2012 and was made generally available on November 1, 2012.[16] As of September 23, 2012, all students subscribed to DreamSpark program can download Windows Server 2012 Standard or Datacenter free of charge.
Thursday, 1 September 2016
Wednesday, 31 August 2016
About RED HAT 6
Linux Operating system
•It is a system software which provides an interface between user, hardware, peripherals devices and application program. Every os consists of two components
•It is a system software which provides an interface between user, hardware, peripherals devices and application program. Every os consists of two components
•Kernel
•shell
Kernel
•It is core of an operating system, it
is an interpreter between user and hardware. In Dos – 10.sys, msdos.sys, in xp –
NTUSKRMI32.com, in linux – Vmlinuz.
•Shell
•Shall is a command line interface
(interpreter) between user and kernel. In Dos, winxp,
win7,2k8, 2k3, vista – command.com
•In linux and unix – bash, csk,ksh,tcsh.
Types
of operating system
•There are 3 types of operating system.
1.Single user single task – in
this os a single
user log in an perform a single task
Ex. Dos
2.Single user multitask – in
this os include
all type of desktop os which
log in a single user and perform multitask.
Ex.
Xp,win7, ubuntu
3.Multi user multi task – in this
os more
than one user can log in from the
different terminals and perform multiple task.
Ex.
Server 2000,2003, 2008, Redhat
Enterprise Linux,etc.
File System Structure In Linux
•1. / – Root
•It is a home folder of
an administrative account in linux
Every single file and directory starts from
the root directory.
Only root user has write privilege under this
directory.
2. /bin – User Binaries
•It store all the
binaries files
Contains binary executables.
Common linux commands
you need to use in single-user modes are located under this directory.
Commands used by all the users of the system
are located here.
For example: ps, ls, ping, grep, cp.
•3. /sbin – System Binaries
•It store all the
system binaries
•All the adminsitrative commands such as user add user mode, user del, grp del & grp add etc
Just like /bin, /sbin also
contains binary executables.
•4. /etc –
Configuration Files
Contains configuration files required by all
programs.
This also contains startup and shutdown shell
scripts used to start/stop individual programs.
For example: /etc/resolv.conf, /etc/logrotate.conf
•5. /dev – Device Files
•It is store all the
hardware access point .
Contains device files.
These include terminal devices, usb, or any
device attached to the system.
For example: /dev/tty1, /dev/usbmon0
•6. /proc – Process Information
•It stores all the virtual file system , process in the system
Contains information about system process.
7. /var – Variable Files
var stands
for variable files.
Content of the files that are expected to grow
can be found under this directory.
This includes — system log files (/var/log);
packages and database files (/var/lib);
emails (/var/mail);
print queues (/var/spool);
lock files (/var/lock);
temp files needed across reboots (/var/tmp);
•8. /tmp – Temporary Files
Directory that contains temporary files
created by system and users.
Files under this directory are deleted when
system is rebooted.
•9. /usr – User Programs
•It store user
documentation and manual pages.
Contains binaries, libraries, documentation,
and source-code for second level programs.
/usr/bin
contains binary files for user programs. If you can’t find a user binary under
/bin, look under /usr/bin. For
example: at, awk, cc,
less, scp
/usr/sbin contains
binary files for system administrators. If you can’t find a system binary under
/sbin, look
under /usr/sbin. For
example: atd, cron, sshd, useradd, userdel
/usr/lib
contains libraries for /usr/bin and
/usr/sbin
/usr/local
contains users programs that you install from source. For example, when you
install apache from source, it goes under /usr/local/apache2
•10. /home – Home
Directories
•It is store the home
directory of the local user account with there name .
Home directories for all users to store their
personal files.
For example: /home/john, /home/nikita
•11. /boot – Boot
Loader Files
it stores booting files of the operating system
Contains boot loader related files.
Kernel initrd, vmlinux, grub
files are located under /boot
12. /lib – System Libraries
It store all the library files
Contains library files that supports the
binaries located under /bin and /sbin
Library filenames are either ld* or lib*.so.*
For example: ld-2.11.1.so, libncurses.so.5.7
•13. /opt – Optional
add-on Applications
opt stands for optional.
Contains add-on applications from individual
vendors.
add-on applications should be installed under
either /opt/ or /opt/ sub-directory.
•14. /mnt – Mount Directory
Temporary mount directory where sys admins can
mount filesystems.
•15. /media – Removable
Media Devices
Temporary mount directory for removable
devices.
For examples, /media/cdrom for
CD-ROM; /media/floppy for floppy drives; /media/cdrecorder for CD
writer
•16. /srv – Service Data
srv stands
for service.
Contains server specific services related
data.
For example, /srv/cvs contains
CVS related data.
swap
partition
•The swap partition is the portion of
the hard drive that linux uses as
virtual memory when it runs out of physical memory.
•Swap partition is a dubal of the
RAM